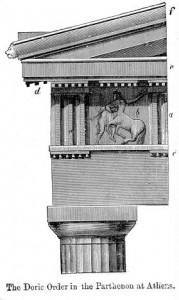
Doric
The Ancient Greeks recognised three distinct orders – the Doric, Ionic and Corinthian – to which the Romans added the Tuscan and the Composite. Of the Greek orders the Doric is the most squat, with a round capital and no base. The column has 20 grooves or flutes and above the square abacus the entablature consists of a smooth lower section with alternating triglyphs and metopes above. The triglyphs consist of three vertical bands and the metopes are relief sculptures.
Slide 1: Parthenon, W facade

Parthenon West facade
Slide 3: Temple of Apollo, Corinth

Slide 4: Basilica, Paestum
Slide 5: Temple of Zeus, Olympia
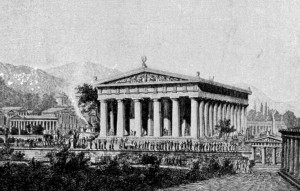
Imagined reconstruction of the Temple of Zeus, now destroyed.
Slide 6: Doric order of the Parthenon
Slide 7: Origins of Doric, diagram (image not found)
Slide 8: Temple of Aphaia, Aegina
Slide 9: Aegina, detail of corner

Slide 10: Libreria, Venice, detail of corner
Slide 11: Temple of Athena, Delphi, capital
Slide 12: Temple of Aphaia, Aegina, capital
Slide 13: Temple of Zeus, Olympia, capital
Slide 14: Temple of Athena, Tegea, capital

Ionic
Slide 15: Ionic order, diagram
Slide 16: Temple of Athena, Priene
http://www.goddess-athena.org/Museum/Temples/Priene/Priene_Sanctuary_Reconstruction.jpg
Slide 17: Temple on the Illissos, Athens(image not found)
Slide 18: Erectheion, Athens, north porch
Slide 19: Erectheion, Athens, capital

Slide 20: Erectheion, column base

Slide 21: Temple of Artemis, Ephesos, capital
Slide 22: Temple of Artemis, Ephesos
Slide 23: Temple of Artemis, Sardis, capital
A portion of the classical temple to Artemis at the site of Sardis in western Turkey. This city, once the capital city of the Lydian Empire became the Persian capital of Asia Minor after the defeat of the Lydians by the Persians in 546 BC. The cliffs in the background show where the ancient citadel was once located.
Slide 24: Asklepeion, Pergamon, capital
Slide 25: Temple of Athena Nike, Athens
Slide 26: Temple of Athena Nike, Athens
Slide 27: Temple of Athena Nike, Athens, frieze

Slide 28: Temple of Athena Nike, Athens, capital
Slide 29: Temple of Artemis, Ephesos, plan
Slide 30: Temple of Zeus, Olympia, plan
Slide 31: Temple of Artemis, Magnesia
Slide 32: Temple of Artemis, Magnesia, plan
Slide 33: Temple of Apollo, Bassae
Slide 34: Temple of Apollo, Bassae, interior
The single central column is pre – Corinthian in style
Corinthian
Slide 35: Temple of Apollo, Bassae, Corinthian cap.
It is the first nearly complete temple still surving, with for the the first time, all three architectural styles: Doric, Ionian and Corinthian. The temple was erected on a raised area, 1,131m, called the ‘Bassai ‘, meaning little vale in the rocks.
It is a Doric peripteral temple made from local limestone, and consists of a prodome and a cella. It is orientated north to south. In the cella there was a column with a corinthian capital, which is the oldest known example of its kind.
The temple was decorated with a marble sculpted frieze depicting the battles between the Amazons and the Centaurs. The frieze ‘s marbles have been looted by the British and can now be found in the British Museum.
The temple, work of Ictinos architect of the Parthenon, is dated at ca. 420 B.C. It was built over an older temple, by the inhabitants of Figalos in honour of Epicurean Apollo, gratitude for saving them from a plague. The name Epicuros was given to Monument of Lysicrates, Athens
Slide 38: Tholus, Epidauros, capital
Slide 39: Temple of Athena, Tegea, capital

Slide 40: Temple of Athena, Tegea, section(image not found)
Slide 41: Maison Carée, Nimes

Slide 42: Arch of Titus, Rome, Composite capital

Use of the Orders
Slide 43: Temple at Assos, entablature
Slide 44: Temple at Assos, facade
Slide 45: Bouleterion, Miletos, capital(image not found)
Slide 46: Arch of Augustus, Rome, capital
Slide 47: Temple of Aphaia, Aegina, interior
Slide 48: Parthenon, section
Slide 49: Propylaea, Athens, plan
Slide 50: Propylaea, Athens, facade
Slide 51: Propylaea, Athens, interior(image not found)
Slide 52: Propylaea, Athens, column bases(image not found)
Slide 53: Parthenon, E facade
Slide 54: Parthenon, stylobate
Slide 55: Parthenon, diagram of refinements(image not found)
Slide 56: Erectheion, Athens, general view
Slide 57: Erectheion, west facade
http://www.perseus.tufts.edu/cgi-bin/architindex?lookup=Athens,+Erechtheion
Slide 58: Erectheion, caryatid porch(image not found)
Slide 59: Colosseum exterior
Slide 60: Pont du Gard
Slide 61: The Orders
http://www.cmhpf.org/kids/Pix-n-stuff/Doric.gif
Slide 62: Tempietto, S.Pietro in Montorio, Rome
The Tempietto (1502) was designed by Donato Bramante, one of the greatest architects of the Italian Renaissance. The building, with a domed rotunda and surrounded by columns, was commissioned by Ferdinand and Isabella of Spain to commemorate St. Peter’s crucifixion. It is located in Rome, in a convent called San Pietro in Montorio.


